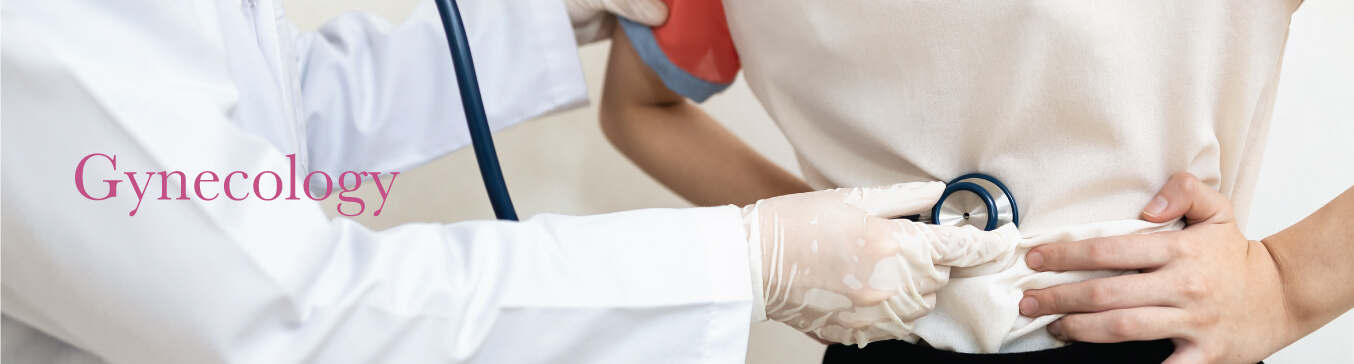

- General Gynecology
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Female Sexuality Issues
- Fibroids
- Uterine Vaginal Disorders
- Menstrual Disorders
- Endometriosis
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Abnormal Bleeding
- Menopause
- Pelvic Floor Issues
- Cystocele
- Bowel Incontinence
- Lower Genital Tract Dysplasia
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
- Rectocele
- Urinary Incontinence
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
- Contraception
- Gynaecological Cancers
- Family Planning
- General Gynecology
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Female Sexuality Issues
- Fibroids
- Uterine Vaginal Disorders
- Menstrual Disorders
- Endometriosis
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Abnormal Bleeding
- Menopause
- Pelvic Floor Issues
- Cystocele
- Bowel Incontinence
- Lower Genital Tract Dysplasia
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
- Rectocele
- Urinary Incontinence
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
- Contraception
- Gynaecological Cancers
- Family Planning
Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence is a condition when there is a loss of bladder control, a common and often socially uncomfortable condition. This could include an occasional trickling of urine on coughing or sneezing or result in a sudden urge, where one would have to rush to use the toilet, unable to hold.
Incontinence occurs due to various reasons. Stress incontinence is when there is a leakage of urine due to pressure exerted on the bladder – like by coughing, sneezing, laughing, lifting weights etc. Urge Incontinence is when there is a sudden urge to urinate, which unless addressed, results in an involuntary loss of urine. It is also possible there is an urge to urinate often, even throughout the night. This is often due to an infection, a neurological issue, or diabetes.
Other types include Overflow Incontinence where there is constant dribbling of urine and the bladder doesn’t empty completely. Functional Incontinence, where other health conditions make it difficult for one to reach the toilet in time such as in the case of wheelchair bound individuals. Mixed Incontinence when more than one condition is contributing to the cause.
Urinary incontinence is caused due to various reasons. Common ones include UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) where the bladder could be irritated causing a strong urge, and Constipation, where hardened stools could cause the nerves to become overactive, increasing the frequency of urine.
Other causes are Pregnancy, where hormonal changes and increased weight could result in Stress incontinence, and Childbirth, where a vaginal delivery can weaken the muscles that control the bladder nerves, and supportive tissue.
Other common causes include age, where the bladder muscle loses the capacity to store and sustain urine, Menopause when women produce less estrogen, the hormone responsible for keeping the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy, leading to a deterioration of these tissues.
Certain Neurological disorders like Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, brain tumour or spinal injury can also impact the nerve signals that govern bladder control, leading to urinary incontinence.
Incontinence usually occurs as people get older though it is not a norm. One must see a doctor if the condition persists for long or aggravates over time, affecting day-to-day activities. Often, simple lifestyle and dietary changes or exercises can address the condition. Other approaches include controlling weight, avoiding spicy food and bladder irritants such as coffee, alcohol and acidic food. But if it still persists enough to hinder your daily routine, do consult our doctors. Our specialist team at Motherhood Hospitals will conduct the required diagnostics, identify the cause, and help you address/ manage it.
DOCTORS

Dr. Kavya Krishna Kumar
MBBS, FMAS, MS
Consultant - Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Alwarpet, Chennai

Dr. Sireesha Reddy
MBBS, CCT, MD (OBG), FRCOG
Consultant - Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Bangalore, Hebbal

Dr. Dhanalakshmi R.
MBBS, DNB (Paediatrics), MRCP CH, Followership in Neonatal Neonatal medicine(UK), PGPN (USA), IPPN, ACLP
Consultant - Neonatology & Paediatrics
Bangalore, HRBR Layout
























































 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number