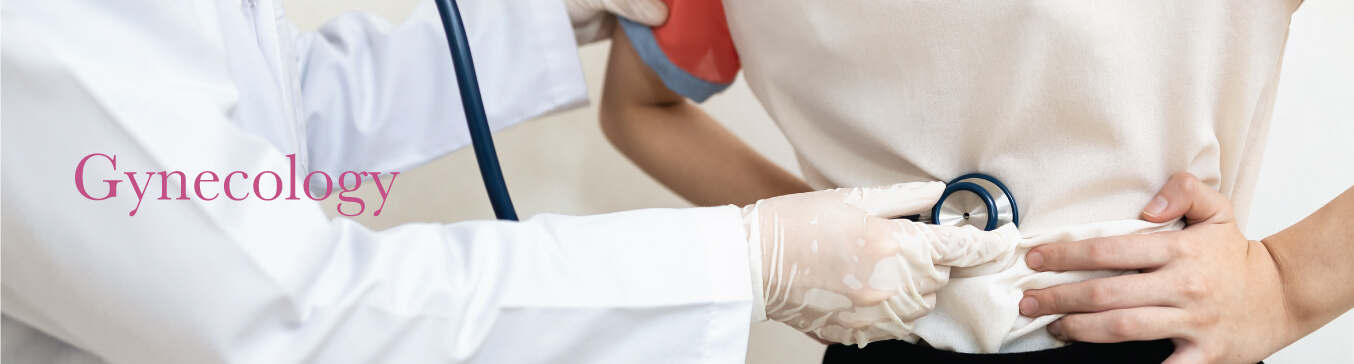

- General Gynecology
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Female Sexuality Issues
- Fibroids
- Uterine Vaginal Disorders
- Menstrual Disorders
- Endometriosis
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Abnormal Bleeding
- Menopause
- Pelvic Floor Issues
- Cystocele
- Bowel Incontinence
- Lower Genital Tract Dysplasia
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
- Rectocele
- Urinary Incontinence
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
- Contraception
- Gynaecological Cancers
- Family Planning
- General Gynecology
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Female Sexuality Issues
- Fibroids
- Uterine Vaginal Disorders
- Menstrual Disorders
- Endometriosis
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Abnormal Bleeding
- Menopause
- Pelvic Floor Issues
- Cystocele
- Bowel Incontinence
- Lower Genital Tract Dysplasia
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
- Rectocele
- Urinary Incontinence
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
- Contraception
- Gynaecological Cancers
- Family Planning
Cervical Cancer
Cancer that occurs in the cells of the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina called the cervix is medically termed as cervical cancer. The vital role in causing cervical cancer is played by strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection.
When your body is exposed to HPV, its immune system starts the counter system to prevent the virus from causing any harm. However, the virus keeps surviving for years in a small ratio of people further leads to some cervical cells turning to cancer cells.
Symptoms
Early stages of cervical cancer usually go undetected showing no signs or symptoms, however, the advanced stage can show the following symptoms:
- Vaginal bleeding after having sex, during periods or post menopause
- A bloody and watery discharge from the vagina with a foul odour
- Pelvic pain or pain during sex
Causes
The initial build-up state of cervical cancer starts with health cells of the cervix developing mutates in their DNA. A cell’s DNA consists of a set of instructions that instruct a cell the further actions. The real cause of cervical cancer is still unclear; however, the role of HPV is certain in it.
HPV is a common occurrence however the majority of people with this virus never tend to develop cancer. This means that there are other factors such as lifestyle choices or environment that are also contributing to the development of cervical cancer.
Risk factors
- Multiple sexual partners
- Early sexual activity
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Weak immune system
- Regular smoking
Prevention
- Ask the doctor regarding the HPV vaccine: HPV infection can be prevented with vaccination which will further reduce the risk of cervical or HPV-related cancer.
- Regular Pap tests: Pap tests are effective in detecting precancerous conditions of the cervix so that cervical cancer can be prevented.
- Safe sex: cervical cancer can be avoided by following safe measures of intercourse such as using a condom or reducing the number of sexual partners to avoid sexually transmitted infections.
- Stop smoking: it’s good if you’re not smoking and if you do, get in touch with your doctor to work on quitting smoking strategies
DOCTORS

Dr. Kavya Krishna Kumar
MBBS, FMAS, MS
Consultant - Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Alwarpet, Chennai

Dr. Sireesha Reddy
MBBS, CCT, MD (OBG), FRCOG
Consultant - Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Bangalore, Hebbal

Dr. Dhanalakshmi R.
MBBS, DNB (Paediatrics), MRCP CH, Followership in Neonatal Neonatal medicine(UK), PGPN (USA), IPPN, ACLP
Consultant - Neonatology & Paediatrics
Bangalore, HRBR Layout
























































 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number