
COVID-19, its prevention, vaccination and breastfeeding your child


COVID-19 infection went ahead to infect millions worldwide. WHO identified COVID-19 as a pandemic and a threat to the global economy. Pregnant women with COVID-19 are 5 times more prone to get admission in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) or end up on a ventilator than the nonpregnant counterparts. Though preterm birth may be a risk in pregnant women with severe COVID-19 complications, other obstetric complications like stillbirth or neonatal mortality aren't evident. Some pregnant women may develop severe illness from COVID-19 infection in various scenarios. They may include factors such as advanced maternal age, risky body mass index, pre-existing conditions like hypertension, diabetes or other pregnancy-specific conditions.??
What are the facts about taking a COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy?
Your obstetrician will guide you about the benefits and potential risks (if any) based on your overall medical history.?
- A pregnant lady who had received vaccination previously and is up to taking the next or second dose in pregnancy should take the second dose of the same vaccine. It's recommended specifically if the vaccine didn't create any disruptions or side effects.?
- COVID-19 vaccine is capable of preventing 95% of COVID-19 infections.
- COVID-19 vaccine will allow you to stay healthy avoiding the infection and keep the people around you from contracting the virus.
- COVID-19 vaccine doesn't contain any constituents rendered harmful for maternal or foetal health.
- No serious contraindications or side effects are seen as yet. However, a few people may develop mild to moderate side effects such as:
A. Fever. B. Joint pain C. Chills D. Headache E. Fatigue F. Reactions on the site of infection including pain and soreness. G. Doldrums
- High fever is one of the possibilities in about 1% of the people who take the vaccine.
- Persistent high fever may create health issues in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Owing to the serious complications of COVID-19, some pregnant women may be at the risk of spontaneous miscarriage or congenital malformations.?
- If your obstetrician says that you may be at risk, you may consider deferring the vaccine until after the first trimester.?
- You should try to update yourself about COVID-19 and its vaccine.
Are there any contraindications associated with the COVID-19 vaccine?
Every vaccine has its impacts. If you develop an allergic response to the vaccine or any of its constituents, avoid the vaccine. However, you should stay in touch with the latest developments. No evidence suggests that COVID-19 vaccines may induce side effects harmful to conception. Your obstetrician may guide you about how to start your preparations for pregnancy based on your medical history. If you have a history of vigorously reacting to any vaccine, you may discuss the same with your obstetrician.?
Is it right to avoid the COVID-19 vaccine only owing to the fear of birth defects?
The outset of every pregnancy marks a 3-5% chance of sustaining birth defects. The phenomenon is known as background risk. According to various analyses worldwide, a COVID-19 vaccine may not raise the risk of birth defects. If your obstetrician recommends the vaccine based on the benefits that outweigh the risks of COVID-19, take the vaccine.?
Who is at a mild to moderate risk of severe COVID-19 illness?
- People with a mismanaged or dysregulated blood pressure
- Immunodeficient people.
- People with various chronic inflammations and under treatment for inflammatory conditions
- People with neurological issues including dementia or stroke
- People who are obese
- People who are suffering from a chronic liver disease
- People grappling with diabetes
- People with a non-haematological cancer
- People with a respiratory illness including chronic lung diseases
- People with renal issues or chronic renal diseases
- People suffering from myocardial infarction or with a history
Who is at severe risk of COVID-19 infection?
- People undergoing intense therapy session including Chemotherapy or radiotherapy
- People with haematological cancers diagnosed within the last 5 years including lymphoma, myelodysplastic syndrome, leukaemia?
- People undergoing immunosuppression for illnesses such as Graft versus host disease
- People who underwent a bone marrow transplant in the last 2 years
- People who underwent organ transplant?
- People who are undergoing immunosuppression after an organ transplant?
You may have to consider various factors if you think you are vulnerable to side effects:
- If you have health conditions making you prone to severe complications after your exposure to COVID-19.
- If you can adopt work-from-home culture or have already adopted towards the reduction of COVID-19 risk.
- Try studying your health based on your medical history.
- Discuss with your obstetrician about your comfort level.
- Tell your obstetrician when you are more comfortable taking the vaccine.
- If you think you are comfortable taking the vaccine in the first trimester, make sure your obstetrician approves of your decision.
- If you are afraid of developing complications after taking the vaccine in the first trimester, tell so your obstetrician.
- If you defer taking the vaccine, make sure you take it as planned in the second trimester.
- Even if you prefer to defer the vaccination until after childbirth, make sure your obstetrician is aware of it.
- And even if you go ahead to defer the vaccine, your decision won't affect the quantum of care you receive from your obstetrician or healthcare provider.
Possible effects of receiving COVID-19 vaccine after another vaccine:
Your obstetrician may highlight the importance of various vaccines. Tdap and Flu shot are generally recommended in pregnancy. If you prefer to take the vaccine during pregnancy or postnatal phase, you should schedule it at least 14 days before or after another vaccination.?
Effects of COVID-19 Vaccine during breastfeeding:
The vaccine will be available for all who wish to take it. The data available currently about the impacts of the COVID-19 vaccine taken by mothers on their babies is unclear. The constituents of any vaccine entering int the breastmilk may be dissolved quickly after the milk gets digested. Apart from everything else, your immune response may get transferred to the baby after you take the vaccine.?
What about the women who discover that they are pregnant during or after vaccination?
Those who discover that they are pregnant during vaccination or after being vaccinated shouldn't be advised to terminate their pregnancy. If a lady discovers that she is pregnant during the vaccine drive (after the first dose, and ahead of the second one), the decision should depend on the analysis of the potential risks.?Motherhood hospital takes sincere efforts to ensure stress-free childbirth.
Related Blogs
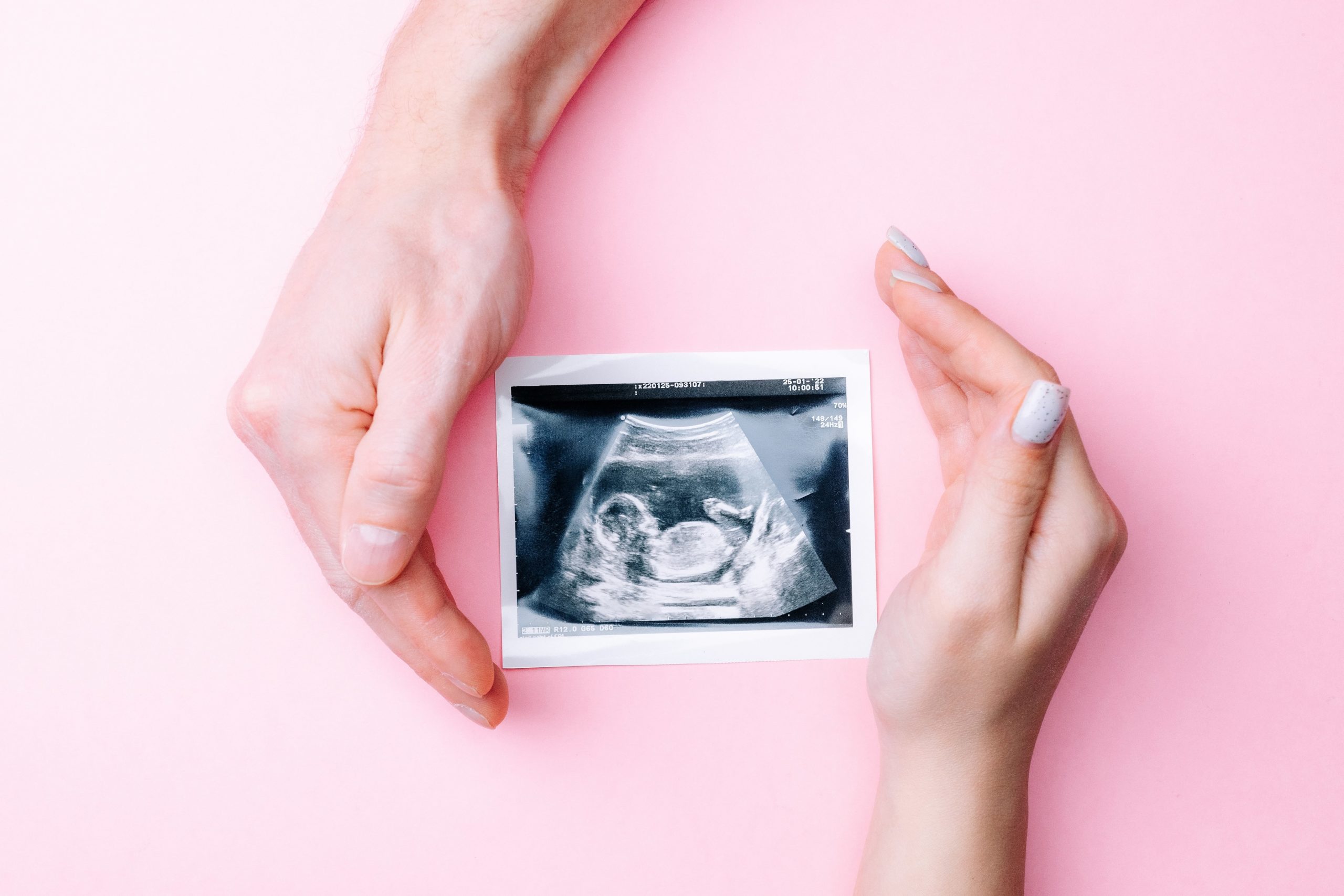
NT Scan During Pregnancy: A Crucial Early Screening Test for Your Baby's Health
Read More
Boosting Fertility: A Guide to Conception Calculators and Ovulation Tracking
Read More
Understanding Different Types of Vaginal Birth Delivery
Read More
How to Treat and Prevent Brown Discharge
Read More
Endometriosis Understanding, Diagnosing, and Managing the Condition
Read More
Emotional Support During IVF Treatment
Read More
Understanding Gestational Diabetes: Insights from Dr Shruthi Kalagara
Read More
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Pregnancy
Read More
Early Pregnancy Care for New Pregnant Women: Expert Advice | Motherhood Hospitals
Read More
Body Positivity Tips Post C Section (Cesarean Delivery)
Read MoreRequest A Call Back
Leave a Comment:
View Comments
Previous
Next
HELLO,
Stay update don our latest packages, offer, news, new launches, and more. Enter your email to subscribe to our news letter


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number





No comment yet, add your voice below!