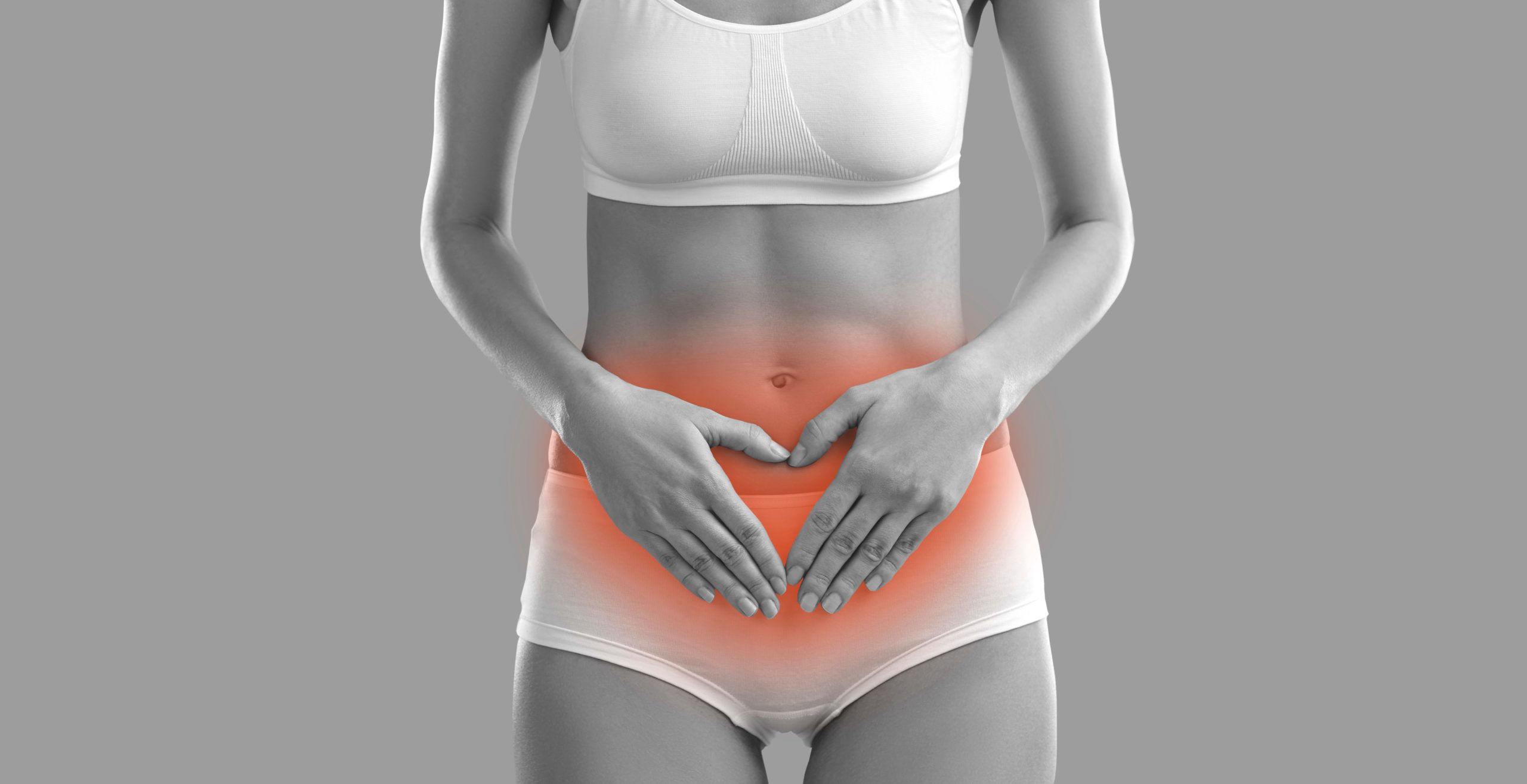
Hernia is a hole or gap in the abdominal muscle wall that causes either intestine or fatty tissue to protrude through.
Areas of Hernia: Abdomen, Groin, Incisional sites.
Hernia types:
- Umbilical or belly button: Umbilical Hernia is the most common of Hernias in pregnancy. It is the site where umbilical cord is attached when child is born. There is a small opening in this area and an increased pressure can stretch it open. It appears in pregnancy and disappears after delivery.
- Inguinal hernia/Femoral hernia: These are seen in the groin area.
- Incisional hernia: It develops in the operation site, and is usually seen in vertical scar on abdomen.
Hernia normally occurs after 18-20 weeks of pregnancy and around 2% of women get Hernia during or after their pregnancy. Approximately 0.02% of women require surgery.
2 per 1000 women with transverse incision and 10 to 30% women with vertical incision can get hernia.
Hernia in pregnancy does not require immediate attention, unless it becomes painful. If painful and left untreated can lead to serious and life-threatening complications like obstruction and intestinal gangrene.
Babies may not get affected by mothers Hernia.10-30% of infants have umbilical hernia after birth which usually closes by 1 year and 2% remain which may require surgery.
Predisposing factors:
- Women having muscle weakness from birth.
- Aggregating factors like chronic cough, constipation, asthma and obesity
- Big baby, twins, polyhydramnios can also stretch muscle making them thin and weak, and tear them due to pressure of growing baby in uterus.
- Heavy weight lifting.
- Fluid in the abdomen.
- Tumor in the abdomen raising intra-abdominal pressure.
Signs and symptoms of Hernia:
Many women have no symptoms. Some can see or feel a bulge while lying down, standing or coughing, in the inguinal or belly button area. Some have dull aching pain while laughing talking, coughing and sneezing. Some may find difficult to walk if they become bigger. If symptoms like pain, fever, nausea are there, they should meet the doctor immediately.
Diagnostic tests:
- By physical examination on inspection and palpation feeling the gap in the hernia site and reducing the contents back into the abdomen.
- By cough impulse one can feel the touch of the intestine gurgling in the hernia site.
- Ultrasound examination of abdomen and pelvis can show the site, size, shape and contents of the gap. Higher test like CT scan also be done.
Treatment of hernia:
Once detected treat with good physical support at the site of a hernia to prevent the further discomfort. Hernia support band, compression therapy groin bands etc to be used under Doctor??s supervision. While sleeping take off the hernia support band. Keep pillow between or under knees for support.
It??s not recommended to have surgery during pregnancy unless its posing risk to the mother and baby. If due to some complication, surgery has to be done, plan it in second trimester of pregnancy. This carries a risk of preterm delivery.
For Pregnancy with Hernia, Caesarian section is not mandatory, they can deliver normally. Caesarian section is done only if obstetrics reasons are there. After delivery allow the body to recover fully which can be from 3 to 6 months. Then surgery can be done, if Hernia persists.
Tips for Prevention:
- Go for pre-conception counseling which includes general and physical examination to rule out Hernia.
- Minimize excess physical activity like lifting heavy weight.
- Yoga and muscle strengthening exercises under guidance
- Maintain healthy body weight
- Maintain balance diet, avoid constipation.
- Avoid lifting or carrying children in arm.
- Avoid smoking, and avoid pushing hard during bowel movement or passing urine.
Types of surgery:
- Open method
- Laparoscopic method
In both the methods hernia gap is repaired using a mesh.


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number