Author: Dr. Kavya Krishna Kumar MBBS, FMAS, MS
Consultant – Obstetrician & Gynaecologist at Motherhood Hospitals, Alwarpet

During pregnancy, the fetus and placenta produce certain hormones that make the mother resistant to the insulin produced by her own body. To compensate, the mother has to produce more insulin to maintain the blood sugar levels. When this extra insulin produced is not enough, blood sugar level rises to cause a condition called gestational diabetes.
What Is Gestational Diabetes?
A condition where a pregnant woman’s blood sugar rises is called gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is classified into two categories. The first category is class A1, which can be managed through diet and exercise. The second category is class A2. Pregnant women diagnosed with class A2 need to take insulin and other medications to keep their blood sugar level at a normal level. Although gestational diabetes goes away after delivery, it can affect your baby’s health and can raise the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
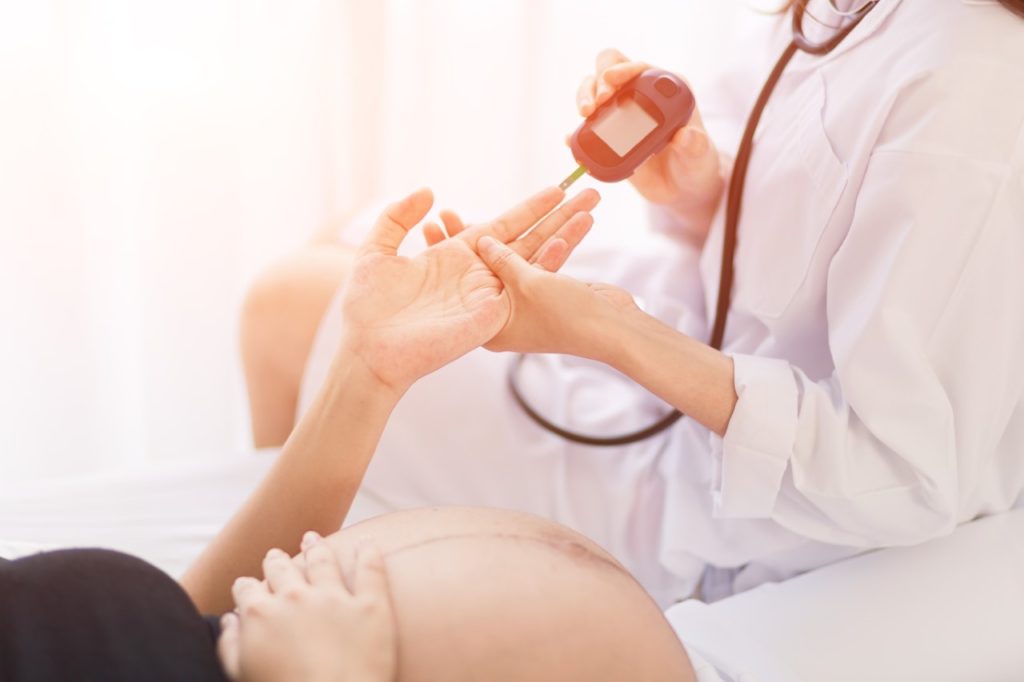

Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
Gestational diabetes does not have any specific symptoms. Most cases are only discovered when your blood sugar levels are tested during screening for diabetes.Some women can develop symptoms,if the sugar levels are too high ,such as..
- You feel more thirsty than usual
- You feel like eating more than you usually do
- Urination is persistent and uncontrollable.
- Tiredness
Gestational Diabetes Causes
The primary function of your pancreas is to release insulin when you eat food. Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose from the blood to the cell so that it can use for energy. Your placenta can produce a variety of hormones which produces insulin resistance leading to increase in blood glucose levels resulting in gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes and pregnancy are very closely associated. Here are some of the risk factors that have high chances of developing gestational diabetes:
- Being overweight before pregnancy
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Prior gestational diabetes in your first pregnancy
- Given birth to a stillborn or with birth defects
- History of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, or other medical complications
- History of PCOS or PCOD or any other health disorder related to insulin.
Risk factors associated with gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes increases the risk of having high blood pressure during pregnancy. It will ultimately affect the baby with issues like a large head which can only be delivered by caesarean section (C-section).
Other effects that gestational diabetes can have on the baby are:
- Overweight at the time of birth (9 pounds or more)
- Premature birth with breathing and other problems
- If you have gestational diabetes, your baby is at a high risk of developing severe breathing issues such as respiratory distress syndrome — a condition that makes breathing difficult.
- Baby may have low blood sugar, which can only be balanced by prompt feedings or, in some cases, intravenous glucose solution.
- The baby may develop Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Usually, women having gestational diabetes return to regular blood sugar levels after delivery. However, 50% of women develop Type 2 diabetes. Therefore, the risk associated with gestational diabetes can be avoided with a healthy diet and maintaining reasonable body weight after delivery.
Treatment for Gestational Diabetes
Treatment for gestational diabetes must be taken as soon as you are diagnosed with it to keep you and your baby healthy, post-delivery. During this treatment, you need to:
- Examine the blood sugar level at least four to five times a day.
- Follow a healthy diet. Dieticians specially design gestational Diabetes diet keeping in mind the body type and condition of your pregnancy.
- Exercise regularly.
- Take urine tests to check for ketones (chemicals that determine whether your diabetes is under control or not)
The doctor will keep a close track of your weight and your baby’s healthy development. If required, they may give you insulin or certain other medications to keep your blood sugar normal.
Exercise and Diet for Gestational Diabetes
You can maintain the gestational diabetes blood sugar levels by taking good care of the diet and following proper exercise plans.
You need to:
- Replace sugary snacks like ice cream, biscuits, candies and so on with natural sugars like fresh fruits. Eating fresh vegetables, fruits and whole grains in a proper proportion is highly recommended.
- Maintain the habit of having small meals and snack meals at least twice or thrice a day.
- Organise an exercise plan for yourself. Daily exercise can help burn excess fat.
At Motherhood Hospitals, we have a team of experienced super specialists backed by the latest in infrastructure and facilities. We have the best experts in Alwarpet, Chennai. We are experts in handling complex deliveries, gynaecological, and other surgeries including a range of laparoscopic surgeries.
Do take an appointment with the best Gynaecology hospital in Alwarpet, Chennai at a centre closest to you. Meet with our doctors who will carry out the required investigations, diagnose the issue and recommend the most appropriate treatment, enabling you to lead an active life.
If you wish to get in touch with Dr. Kavya Krishna Kumar, please book your appointment here.


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number