BMI (Body Mass Index) Introduction
Body mass index or BMI is a medical screening tool that is used to measure the ratio of your height to weight to estimate the amount of body fat. It is usually calculated by using weight in kilograms (kgs) divided by the square of height in metres (m2). You’ll know more about BMI Calculator formula below.
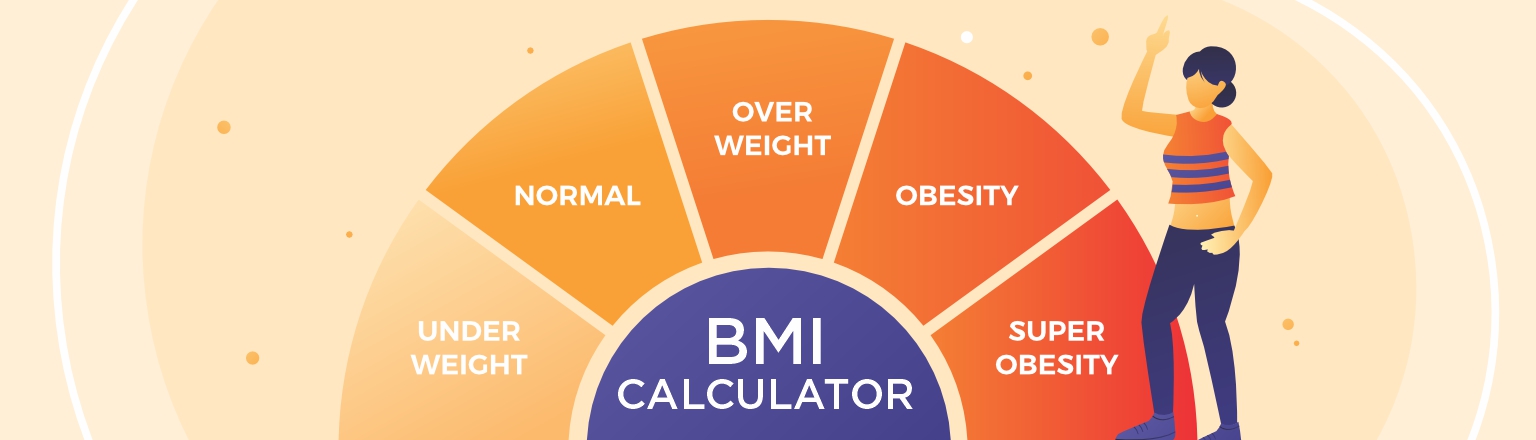
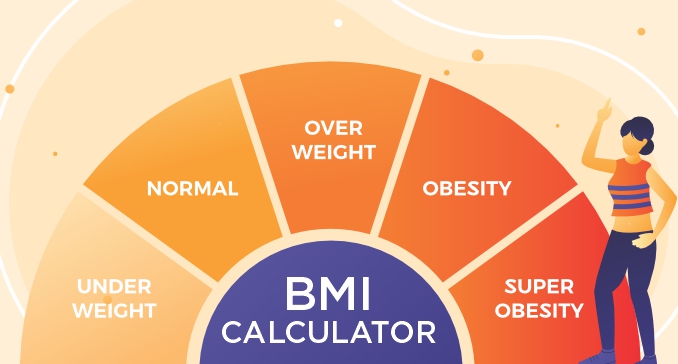
What is the BMI (Body Mass Index) Calculator?
A BMI calculator is used to calculate the BMI value of any individual. In general, the BMI calculator measures your leanness or corpulence based on your height and weight and quantifies tissue mass. It is a popular indicator of whether you have a healthy body weight for your height.
The values generated by the BMI Calculator formula categorize people into underweight, normal weight, overweight or obese depending on what range your values fall in. These ranges in the BMI chart also vary depending on other factors including region and age.
Being underweight or overweight can impact your body adversely and the BMI calculator kg with age is useful in indicating whether you need any additional tests.
BMI Table for adults
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended a BMI table for adults based on their body weight. Both men and women aged 20 or older can use this table.
| Classification | BMI Range |
| Underweight | Below 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 - 24.9 |
| Overweight | 30 - 35 |
| Obese | Above 35 |
BMI table for children and teens, age 2-20
The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has categorized the ideal BMI percentile range for children and teens between the ages of 2 to 20 years.
| Category | Percentile Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | <5% |
| Healthy weight | 5% - 85% |
| At risk of overweight | 85% - 95% |
| Overweight | >95% |
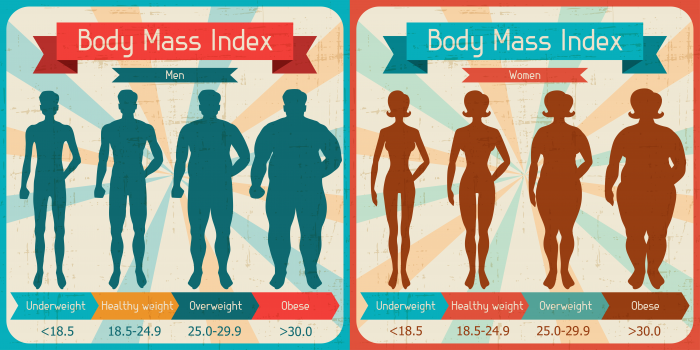
What is the Ideal BMI for Men and Women?
If you are wondering whether there’s a different BMI calculator for men and a BMI calculator for women, there’s no such thing. The ideal BMI for both men and women is the same. Ideally, a healthy BMI range is between 18.5 to 24.9 which comes under the healthy weight category.
Risks Associated with Being Underweight
If you calculate your BMI and it falls under the underweight category, you might be at risk of:
- Malnutrition, Anaemia, and Vitamin Deficiencies.
- Osteoporosis may cause weakness in bones and an increased risk of fractures.
- Reduced immune function.
- Growth and developmental issues specifically in children and teens.
- Reproductive issues in women due to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the menstrual cycle.
- BMI calculator for females may also show chances of miscarriage in the underweight category.
- Complications due to surgery.
Being underweight is nowhere good, instead, in some cases it may also be a sign of an underlying disease or condition including anorexia nervosa. If your BMI is too low, consult your doctor and get yourself checked. The doctor will prescribe you certain medications and create a diet plan for your BMI to fall under the normal range.
Risks Associated With Being Overweight
Similar to being underweight, being overweight has several associated risks:
- High blood pressure.
- High levels of low-density (LDL) cholesterol or bad cholesterol.
- Lower levels of high-density (HDL) cholesterol or good cholesterol.
- Type 2 diabetes.
- Stroke.
- Coronary heart disease.
- Gallbladder disease.
- Osteoarthritis is a joint disorder caused by the breakdown of joint cartilage.
- Sleep apnoea.
- Higher chances of cancer.
- Low quality of life.
- Certain mental disorders including anxiety, depression, and so forth.
- Body pain and difficulty in carrying out daily activities.
Being overweight poses much higher risks and leads to deleterious effects on your body. This is one of the main reasons why you should try and maintain a normal BMI range. In case, your BMI falls under the overweight category, consult your doctor immediately.
How to Maintain a Normal BMI?
An ideal BMI for any individual should fall under the normal range. To maintain a normal BMI, you may have to inculcate:
Healthy Eating Habits
- Focus on consuming a balanced diet including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
- Consume more protein and fibre.
- Limit sugar, salt, and fat intake.
- Avoid overeating and be mindful of your portion size.
- Plan your meals and snacks in a way to avoid impulsive eating.
- Consume at least 4 litres of water throughout the day.
- Maintain a calorie deficit for sustainable weight loss.
Regular Physical Activity
- Engage in moderate physical activity and aim to at least exercise for 150 minutes per week.
- You can also include walking, jogging, or swimming in your exercise regime to improve your cardiovascular health.
- Include strength training exercises to build muscle which can also boost your metabolism.
- Find activities that you enjoy the most.
Behavioural Changes
- Listen to your hunger signs and avoid distractions while eating.
- Eat your food slowly.
- Sleep for at least 7-9 hours per day as poor sleep can also affect your hunger.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
BMI Formula
If you are wondering how to calculate BMI in the first place, below are the simple equations in the International System of Units (SI) and the US Customary System (USC). Both the tools use a 5’10”, 160-pound individual as an example for calculation:
USC Units:
BMI = 703 × mass (lbs)height2 (in)= 703 × 160702= 22.96 kgm2
SI, Metric Units:
BMI = mass (kg)height2 (m) = 72.571.782 = 22.90kgm2
BMI Prime
The WHO and Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have also devised a ratio called BMI prime. BMI prime is the ratio of your measured BMI to the upper limit of BMI that is considered “gold standard” or “normal”. This normal range, however, may differ in countries. In Asia, the upper limit is considered as 25 kg/m2
The formula for calculating your BMI prime:
BMI Prime = BMI / 25
Now, since the BMI prime is in itself a ratio of two BMI values, hence, it is dimensionless. For instance, the BMI calculator for men showed a BMI prime less than 0.74, these men will fall under the category of underweight. Values from 0.74 to 1 are categorized as normal, greater than 1 is overweight, and greater than 1.2 falls under obese. Below is the table for your reference:
| Classification | BMI | BMI Prime |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Thinness | less than 16 | less than 0.64 |
| Moderate Thinness | 16 - 17 | 0.64 - 0.68 |
| Mild Thinness | 17 - 18.5 | 0.68 - 0.74 |
| Normal | 18.5 - 25 | 0.74 - 1 |
| Overweight | 25 - 30 | 1 - 1.2 |
| Obese Class I | 30 - 35 | 1.2 - 1.4 |
| Obese Class II | 35 - 40 | 1.4 - 1.6 |
| Obese Class III | > 40 | > 1.6 |
The main advantage of BMI Prime is that it allows you to quickly check how much of your BMI differs from the normal BMI. Moreover, with these values, you can also easily compare groups of people having different BMI upper limits.
Ponderal Index
Similar to BMI, the Ponderal Index (PI) also measures your leanness or corpulence based on height and weight. The main difference between BMI and PI is cubing used by PI as opposed to squaring by BMI.
BMI is a useful tool. It, however, cannot be relied on when calculating a large population. PI is certainly more complicated than BMI but it is more reliable for use in people with very tall or short heights.
Limitations of BMI
Although BMI is widely recognized for indicating healthy body weight, it still poses certain limitations. The main difficulty with BMI is that it does not take body composition into account. People have a wide variety of body types and muscle distribution, bone mass, and fat, and BMI does not consider these factors. Hence, BMI should not only be relied on for checking your health. You can consider it along with other measurements to determine your health status.
In adults:
BMI is not completely accurate as it measures the amount of excess body weight instead of excess body fat. Furthermore, it is also influenced by some factors including age, gender, muscle mass, activity level, body fat, ethnicity, and so forth.
For instance, the BMI calculator for females may show her in the normal category. She, however, is not active in the daily life. This also means that although the BMI is falling under normal, she may have excess body fat which would be unhealthy. Similarly, athletes or bodybuilders may fall under overweight due to high muscle mass. Since muscle mass is heavier than fat, the BMI may consider them overweight although they might be a healthy weight for their body composition.
Keeping this into account, the CDC mentions:
- Older adults have more body fat than younger adults with the same BMI.
- Women have more body fat than men for similar BMI.
- Muscular people or athletes may have higher BMI due to excess muscle
In children and adolescents:
Similar to adults, BMI also poses limitations among children and adolescents. In this age group, height and the level of sexual maturation can also influence BMI and body fat.
Limitations of BMI as a screening tool
BMI values do indicate risk of certain health disorders including Type 2 diabetes or other heart conditions. It cannot, however, be relied on completely as:
- BMI does not take the location of body fat into account. For instance, fat stored in different areas of the body including the abdomen is linked to greater health issues than excess fat in the thighs.
- BMI does not take a family history of diabetes, blood pressure, and heart disease into consideration.
In essence, BMI can be a great tool for indicating body fat for 90-9% population and can effectively be used along with other measurements to determine your healthy body weight.
Who Should Not Use This Tool?
BMI is not an ideal tool for athletes or people with high muscle mass and pregnant women.
Who discovered BMI?
Adolphe Quetelet, a Belgian scientist, discovered the Quetelet Index, which we call the Body Mass Index. However, his goal was purely mathematical. It was because of the American insurance companies who started using it as a predictor for obesity and wondered what to charge for them, as obesity was causing early deaths from a biological perspective.
The WHO noticed that people of Asian descent saw an increased risk of chronic health conditions starting at lower BMI ranges than Europeans. Simultaneously, the WHO observed a trend where Asians’ BMI tends to underestimate their body fat percentage compared to Europeans. So, if we have
a group of Thai people and Italian people, the Italians will have less body fat and a smaller risk of diabetes compared to the Thais of the same BMI.
WHO documented Body mass may not be a good way to predict heart disease in minorities. Risk factors for heart disease are more common at lower BMIs in Black, Hispanic, and Asian populations than in White people.
Body Mass Index: how can it help us? Let us talk about it
BMI is a very widely used tool because it is super easy to measure. We do not need any fancy equipment to measure those, and they are quick and cheap. In most medical practices that are struggling with a lot of patients in a day, this makes a very popular index to categorize people. BMI is quick, cheap, and easy, and in a very general sense, it has a relation with the risk of many health conditions.
How to Calculate BMI?
BMI= Weight [kg] / (Height)2 [m2]
For example, the BMI of a 70 kg man of 175 cm (1.75m) height will be
BMI= 70
1.75 x 1.75
BMI= 22.86 kg m-2
BMI categories
According to the WHO BMI value people can be categorised in 4 different categories 1. Severely Underweight- <16 (cases of starvation and anorexia) 2. Underweight – Below 18.5 3. Healthy weight – 18.5 – 24.9 4. Overweight – 25-29.9 5. Obese- > 30 6. Morbidly Obese->35-40
Classification of obesity based on BMI
1. Obese class I – 30.0-34.9
2. Obese class II- 35.0-39.9
3. Obese class III- ≥ 40
How to use body mass index?
Although BMI has some limitations as it does not specifically measure body composition, the relative amount of fat tissue or lean tissue in the body is a good predictor of weight-related complications across a large population. The farther the BMI is from the normal range in either direction, overweight or underweight, the greater the risk they have of health problems. This is where BMI can be of use.
BMI and pregnancy
A mother’s weight is considered critical for her baby’s survival. Pregnant women with a high BMI are at increased risk. Even a slight increase in a mother’s BMI was associated with an increased risk of fetal deaths, stillbirths, and infant deaths. It may also be a predictor of high blood pressure, diabetes, and preeclampsia, as fat cells produce inflammation within the body.
BMI and pregnancy
A mother’s weight is considered critical for her baby’s survival. Pregnant women with a high BMI are at increased risk. Even a slight increase in a mother’s BMI was associated with an increased risk of fetal deaths, stillbirths, and infant deaths. It may also be a predictor of high blood pressure, diabetes, and preeclampsia, as fat cells produce inflammation within the body.
Why is being fat bad?
Excess fat seeps into the blood, liver, pancreas, muscles, around the kidneys, and in and around the heart. It effectively alters the fuel that the body sees; it applies pressure to the pumps and pipes within your body. It also disrupts some of the filters of your body, i.e., your kidneys and your liver, so that their function is impaired.
What is healthy? BMI alternatives
BMI on its own is not very helpful in determining a person’s health.
It is important to understand the alternatives of BMI as well to have a more efficient health
screening.
Measuring Visceral Fat
Waist Circumference
Assessing genetic metabolic factors
Measurement of Waist to Hip ratio or Waist to Height ratio
How to lower your BMI?
Losing weight is a journey and not a race.
A few relatively minor lifestyle changes can have a dramatic effect on lowering your BMI.
Set realistic and attainable goals: Start by just focusing on 5 percent of your weight. For example, for a 200-pound person, that’s 10 lbs. That means 5 percent weight loss can reduce your chance of diabetes by a whopping 50 percent, not to mention lower your hypertension as well. Once you attain your goal, go for another 5 percent. So, every time you lose 5 percent, remember to slow down and let your body get used to the new routine.
Caloric Density: No matter which diet you chose, at the end of the day you must spend more calories than what you take into your body to lose weight. Watching calories does not mean you have to constantly starve between meals. The key is understanding caloric density, or the number of calories
in each weight of food. Take resins, for example. They are high in caloric density in a small weight of food. In 1 cup of resin, you will consume 500 calories. Grapes, on the other hand, are low in caloric density, meaning they have much lower caloric density in the same weight of food. In 1 cup of grapes, you will be consuming only 62 calories. The point is you can take a lot more grapes to feel fuller and maintain a few calories. Some low-calorie foods that are surprisingly filling are Greek yogurt, egg whites, fish, watermelon, broccoli, popcorn, and skimmed milk.
Exercise: The recommendation is 150 minutes per week of exercise. That is approximately 20 minutes per day. If you are new to exercise, start slowly and work your way up. Ideally, it includes some form of cardio exercise, like walking, running, biking, and swimming, but do not forget about resistance training. Evidence shows lifting weights burns more fat than cardio! A healthy combination of both can help you achieve your goal.
And finally, stay positive. Even the smallest change can make a world difference in overall health.
Your attitude too will help you keep you in the game. Remember, you may not be able to do
everything, but you can always do something.
Conclusion
Owing to the current stressful lifestyle and environmental conditions, obesity has become quite normal at an alarming level. A BMI calculator in India serves as a useful tool to assess your health risks. With a BMI range in hand, your doctor can help you understand its implications and guide you towards a healthy lifestyle choice and prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is recommended to check your BMI periodically especially during a significant change in your life and as a part of your regular health checkup.
BMI is important as it provides a quick way to assess your height and weight ratio. It is a valuable screening tool for identifying several risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese.
BMI is a useful health indicator for 90-95% of people. It, however, does not take muscle mass, fat distribution, and bone density into account.
BMI is a useful health indicator for 90-95% of people. It, however, does not take muscle mass, fat distribution, and bone density into account.
BMI cannot differentiate excess fat, muscle, or bone mass, and fat distribution among people.
Yes, you should be concerned if your BMI is underweight as it may pose certain health complications. Make sure to consult your doctor.


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number