Consultant – Obstetrician & Gynaecologist at Motherhood Hospitals, Sarjapur
Consultant – Obstetrician & Gynaecologist at Motherhood Hospitals, Sarjapur By the time a woman conceives, her body prepares itself for various changes. These changes are important to help a pregnant lady carry her pregnancy to term. A list of changes occurs in the first three months of pregnancy. These occurrences are a precursor to signs that develop throughout all the trimesters.
The first trimester of pregnancy:
The first trimester of pregnancy starts the day a woman conceives and lasts till the 12th week. The need for first-trimester care strikes right here as the first trimester involves crucial changes and challenges. The pregnant lady may gain weight or feel apathetic followed by the common episodes of morning sickness. Various other symptoms associate themselves with the first trimester. It’s a phase that involves quick foetal growth. This is when various vital organs of the foetus develop phenomenally. They include the spine, nervous system and digestive tract. The foetus obtains a human form by the end of the first trimester. A healthy lifestyle is a mandate during the first trimester. Pregnant women may have to maintain dietary control throughout the pregnancy. Pregnant women should seek an obstetrician’s advice early in pregnancy for better outcome (healthy child).
Below are the precautions to take as a crucial part of pregnancy care:
- Hydration – marking your healthy pregnancy:
A rise in blood volume is a significant part of the first trimester. The blood volume increases to actively contribute to the oxygen and nutritional requirements of the foetus. The expectant mother needs more fluids throughout the pregnancy. Various sudden changes in the body warrant a steep rise in the demand for fluid intake. Fresh juices and clean water support you like never before in the pregnancy.
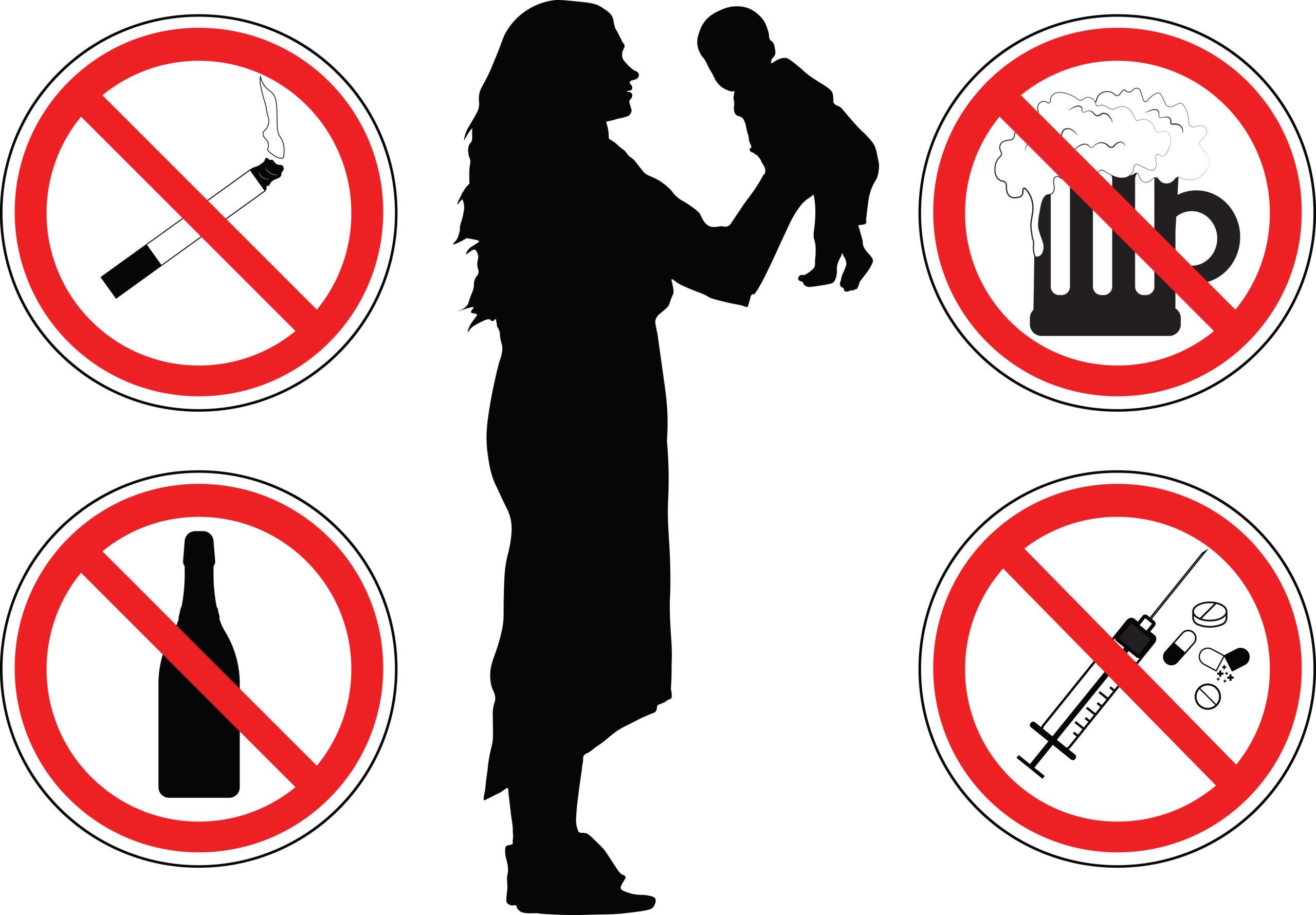
- Stay away from smoking:
Pregnancy is the time when all kinds of addictions negatively influence foetal growth. Smoking in pregnancy raises the risk of miscarriage, premature labour, and ectopic pregnancy. The inhalation of the unhealthy vapours hinders the foetal development risking the overall success of the pregnancy. Practice a lifestyle free of addictions and especially smoking to ensure the safety of yourself and your munchkin.?
- Hb electrophoresis test
- Screening tests may be needed to find out if the baby is at risk for certain inheritable health issues.
- Blood type and antibody screen
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check if you have Anaemia or low platelet count.
- RPR tests to detect any exposure to Syphilis
- Fasting glucose checks for diabetes(HbA1c)
- Prenatal vitamins:
Vitamins play a crucial role in determining the overall status of health. Take prenatal vitamins based on your doctor’s recommendation. The early phase or first-trimester health remains crucial for both mother and her unborn. Folic Acid is the most important supplement as it helps prevent birth defects. Iron helps in the prevention of Anaemia.
- Avoid hot baths and sauna:
High temperatures may interfere with healthy foetal development. Avoid hot showers. Consult your orthopaedic doctor or general physician if you have a history of back pain or joint pain. Some pregnant women can use pads wrapped in a towel to treat their pain. However, it’s important to keep the temperature of the pad below 100-degree F or 37-degree.
- Avoid or restrict seafood:
Seafood is widely accepted as a source of dozens of essential nutrients. Various seafood items contain abundant proteins and fats. But shark, swordfish and other similar fish species contain high levels of mercury. Some seafood items may lead to growth deficits in kids. The first trimester is the best phase to avoid seafood. It’s even better to avoid seafood throughout pregnancy. And if you feel like eating any seafood items in pregnancy, consult the right dietician or your obstetrician.?
- Avoid processed foods:
Majority of the processed foods are dangerous in pregnancy. They contain additives and substances detrimental to foetal development. Many food additives contain traces of sodium nitrate and carcinogenic substances. Pesticides are also known to leach into processed foods. It’s, therefore, essential that you stick to organic foods and avoid packaged items. Make sure that the fruits and vegetables in your kitchen are properly washed and sanitized.
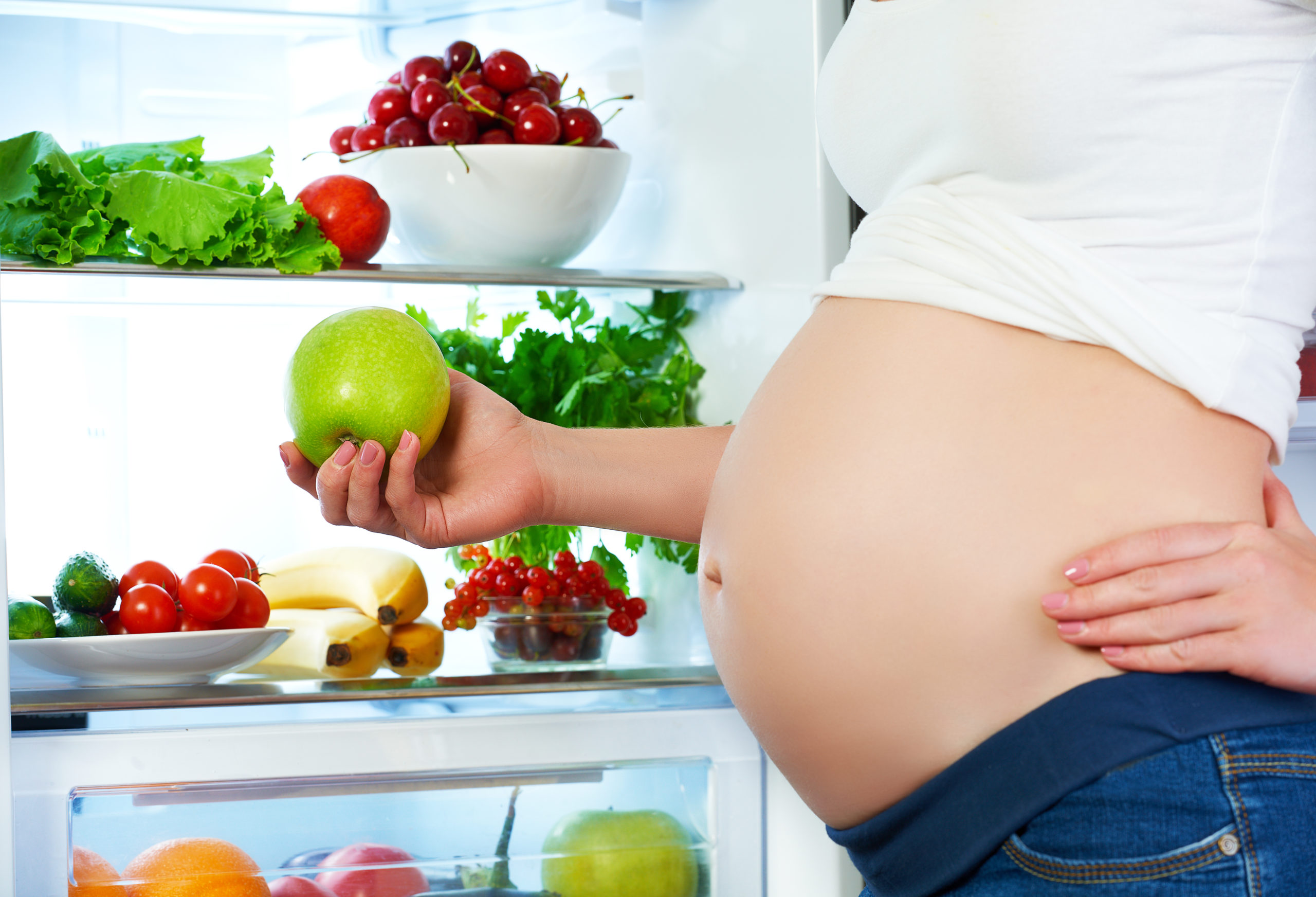
- Be choosy while zeroing your search for the right diet:
Effective weight management and healthy metabolism are the two essential parts of a well-defined pregnancy. And healthy food choices facilitating a balanced diet give you all you expect from a healthy lifestyle. Make sure you are getting abundant vitamin D, mostly from the sunlight. Incorporate more nuts and seeds that fulfil your need for omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids aid the healthy development of your baby’s brain, eyes, and nerves. Include more calcium through spinach, tofu and broccoli. Dairy products are rich sources of Calcium.
- Exercise:
Start with the mild sessions of warm-up or leisurely walks. Avoid brisk walks in the pregnancy. Yoga forms the irreplaceable part of a healthy lifestyle, specifically in pregnancy. Avoid heavy or strenuous exercises that may interfere with your baby’s healthy growth. Some exercises may even lead to preterm labour. Activeness and metabolism are the two essentials of a healthy pregnancy. Light exercises serve the purpose to the fullest, especially during pregnancy.
- Be cautious about prescription medications:
Your obstetrician may scrutinize you for at least 30 minutes if you have a sensitive medical history. He or she may ask you about the prescription medicines you are taking when you are in the first trimester. Some medications may contain teratogens – substances causing birth defects. Antibiotics like streptomycin and tetracycline, anticonvulsants like Coumadin, and Acne medication Accutane are some detrimental medications in pregnancy. It’s better to avoid a different doctor or physician prescribing any medication for you in pregnancy. If you have no other choice, it’s better to consult your midwife/obstetrician.
- Occupational hazards:
If your occupation involves anything risky like handling chemicals such as mercury, it’s better to inform your immediate supervisor. It’s difficult for pregnant women, irrespective of their trimester, to pursue a job that demands strenuous physical effort. Consider taking early maternity leave or cut back on your routine.
- Practice mindful eating during pregnancy:
Practicing mindful eating is a key component of maintaining a healthy and nutritious diet. Mindful eating involves being present and fully engaged in the eating experience, paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, and making conscious choices about the foods you consume. To ensure healthy eating during pregnancy, focus on a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. This means incorporating ample amounts of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. To alleviate nausea during pregnancy, it is advisable to avoid foods that trigger discomfort.


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number