Understanding the Menstrual Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
The menstrual cycle is a natural process that occurs in the female body. It prepares the body for pregnancy every month and involves various hormonal changes. The menstrual cycle typically lasts about 28 days, but it can vary from woman to woman.
Request A Call Back
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5)
This is when bleeding occurs. The uterus sheds its inner lining, leading to menstrual bleeding. This phase can last anywhere from 3 to 7 days.
Follicular Phase (Days 1-13)
This phase begins on the first day of your period and ends with ovulation. The body starts to prepare for ovulation, and several follicles in the ovaries begin to mature.
Ovulation Phase (Day 14)
Around the middle of the menstrual cycle, the matured egg is released from the ovary. This is the most fertile period and the best time for conception.
Luteal Phase (Days 15-28)
After ovulation, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus will be shed, leading to the menstrual phase.
Factors Affecting the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle, while a natural process, can be influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these can help women better manage their cycles and overall reproductive health.
Stress
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, which can delay or even skip menstrual cycles. The body’s response to stress often involves the release of cortisol, a hormone that can interfere with the body’s reproductive hormones.
Weight Changes
Both rapid weight gain and weight loss can impact the menstrual cycle. Being significantly overweight or underweight can lead to irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
Medications
Certain medications, especially those that impact hormonal levels, can affect the menstrual cycle. This includes birth control pills, antipsychotics, chemotherapy drugs, and certain antidepressants.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and endometriosis can lead to irregular or painful periods. It’s crucial to get a proper diagnosis if you suspect an underlying condition.
Lifestyle Factors
Excessive exercise, poor nutrition, and smoking can also influence menstrual regularity. It’s essential to maintain a balanced lifestyle for a healthy menstrual cycle.
Stress
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, which can delay or even skip menstrual cycles. The body’s response to stress often involves the release of cortisol, a hormone that can interfere with the body’s reproductive hormones.
Weight Changes
Both rapid weight gain and weight loss can impact the menstrual cycle. Being significantly overweight or underweight can lead to irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
Medications
Certain medications, especially those that impact hormonal levels, can affect the menstrual cycle. This includes birth control pills, antipsychotics, chemotherapy drugs, and certain antidepressants.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and endometriosis can lead to irregular or painful periods. It’s crucial to get a proper diagnosis if you suspect an underlying condition.
Lifestyle Factors
Excessive exercise, poor nutrition, and smoking can also influence menstrual regularity. It’s essential to maintain a balanced lifestyle for a healthy menstrual cycle.
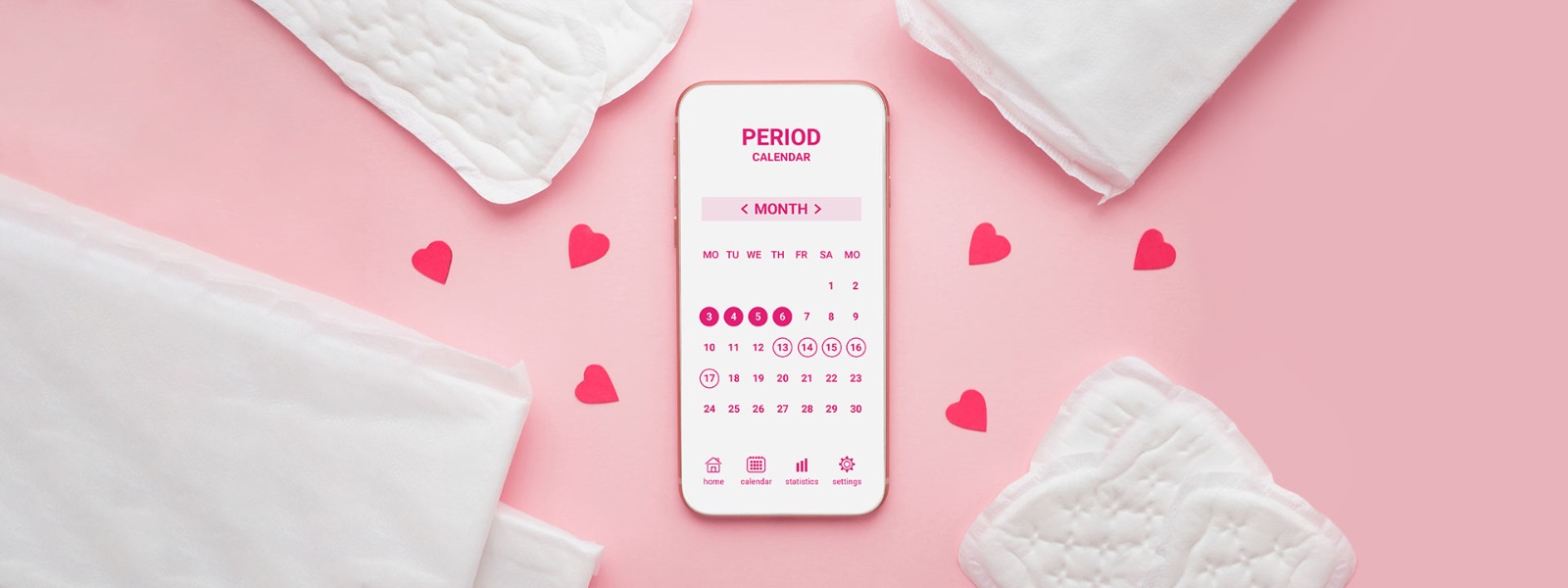
Importance of Tracking the Menstrual Cycle
Understanding and tracking your menstrual cycle goes beyond just predicting your next period. It offers several benefits
Reproductive Health Insights
By tracking your cycle, you can gain insights into your ovulation patterns, menstrual regularity, and any potential irregularities that might need medical attention.
Fertility Awareness
For those looking to conceive, tracking the menstrual cycle can help identify the most fertile days, increasing the chances of conception. Conversely, for those not looking to conceive, it can act as a natural method to avoid pregnancy.
Predicting Menstrual Onset
By understanding your cycle’s patterns, you can better prepare for the onset of menstruation, helping manage both physical and emotional symptoms.
Health Monitoring
Irregularities in the menstrual cycle can be early indicators of health issues like hormonal imbalances, PCOS, or other reproductive health concerns.
Emotional Well-being
For many, menstrual cycles can be linked with mood swings or emotional changes. Tracking these alongside the menstrual cycle can help in understanding and managing emotional well-being.
Reproductive Health Insights
By tracking your cycle, you can gain insights into your ovulation patterns, menstrual regularity, and any potential irregularities that might need medical attention.
Fertility Awareness
For those looking to conceive, tracking the menstrual cycle can help identify the most fertile days, increasing the chances of conception. Conversely, for those not looking to conceive, it can act as a natural method to avoid pregnancy.
Predict Menstrual Onset
By understanding your cycle’s patterns, you can better prepare for the onset of menstruation, helping manage both physical and emotional symptoms.
Health Monitoring
Irregularities in the menstrual cycle can be early indicators of health issues like hormonal imbalances, PCOS, or other reproductive health concerns.
Emotional Well-being
For many, menstrual cycles can be linked with mood swings or emotional changes. Tracking these alongside the menstrual cycle can help in understanding and managing emotional well-being.
Using apps, journals, or even simple calendar markings can aid in tracking the menstrual cycle, making it easier to understand and manage one’s reproductive health.
Tips for Managing Menstrual Discomfort
Many women experience discomfort or pain during their menstrual cycle. Some effective ways to manage this discomfort include:


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number